What is climate change?
Weather is continuously changing, owing to instabilities in the atmosphere. Climate is defined as the average weather condition at a particular place, incorporating such features as precipitation, temperature, windiness, and humidity. The more specific definition would state that climate can be defined as the mean state and variability of elements like temperature, humidity, precipitation, and windiness over some extended time period. Like weather varies from day to day, climate also varies from daily day-and-night cycles up to periods of geologic time.
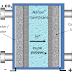
There are natural incidences which fluctuations in the climate, but scientists say temperatures are now rising faster than at many other times. Solar energy radiating/reflecting back to space from the Earth's surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-emitted in all directions. This heat leads to a lower atmospheric and surface temperature of the planet. The Earth's average temperature is about + 15C but due to this effect, the Earth would be about 33C colder and hostile to life.
The world is about one degree Celsius warmer than before widespread industrialization, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). It is believed that between 2005 and 2015, the average sea level increased by 3.6mm per year across the globe.
Climate change is global warming due to the anthropogenic emission of greenhouse gases and the result of a large-scale shift in weather patterns. An increase in global warming is altering the planet's climate systems in countless ways.
Causes of Climate change:
1. Solar variability
The brightness or luminosity of the Sun has been increasing steadily since its formation. As Sun provides the energy to drive atmospheric circulation and constitutes the input for Earth's heat budget, this phenomenon is essential to Earth's climate and plays a significant role in climate change over the time period.
2. Volcanic Activity
It can influence climate in Several ways at different timescales. Volcanic eruptions can release huge quantities of sulfur dioxide and other aerosols into the stratosphere, which reduces atmospheric transparency and thus the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth's surface and troposphere. A
3. Orbital Variation
The orbital variations of Earth's orbit cause changes in the latitudinal and seasonal distribution of solar irradiance, Which drives the number of climate condition fluctuation. Orbital variation plays a significant role in glacial-interglacial and annual monsoonal patterns. The influences of orbital variation have been identified in climatic changes.
4. Tectonic activity
Tectonic activity has changed the shape, size, position, and elevation of the continental masses, as well as the bathymetry of the oceans. Tectonic activity influences atmospheric chemistry, particularly carbon dioxide concentrations (GHG gas). Carbon dioxide is emitted from volcanoes and pour out in rift zones and subduction zones.
5. Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are gas molecules having the property of absorbing infrared radiation emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface as the wavelength becomes longer, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gases.






1 Comments
Thanks for the information
ReplyDelete