Anaerobic digestion is the microbial degradation of organic material under anaerobic conditions. It is unique naturally occurring process, occurs in swamps, hydric soils, landfills, digestive tracks of ruminant animals and termites. During the process, carbon in organic molecules is fully reduced to the methane and functions through synergistic relationships between acid producing and acid consuming microorganism.
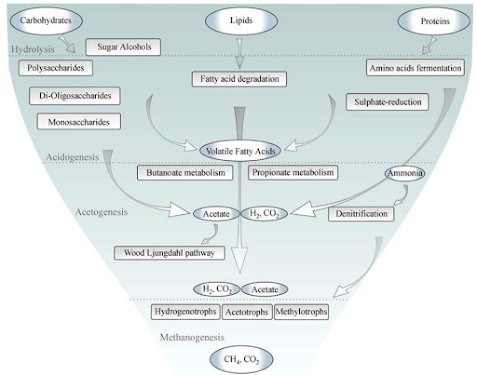 |
fig: Bio-gas production |
Bio-gas through Bio-gas digester includes
- Methane ~ 50-70%
- Carbon Dioxide ~ 30-50%
- Hydrogen, Ammonia, Hydrogen sulfide ~ trace
Alessandro Volta discovered methane in 1776 through studying swamp bottoms.
We can consider digester as black box.
 |
| fig: Bio digester as black box |
 |
fig: Bio-gas production in Digester |
Hydrolysis -Anaerobic digestion
Large organic compounds are broken down into monomeric
compounds. In this process cell are allowed to assimilate materials. Hydrolysis
of particulate biodegradable material is carried on by facultative bacteria
(Eubacterium, Clostridium, Peptococcus etc.)
 |
| fig: Hydrolysis process |
– Carbohydrates are broken down to simple sugars (Glucose…)
– Proteins broken down to amino acids (HOOC-R-NH2
).
– Lipids (include fats, fat-soluble vitamins, waxes,
-glycerides, etc) broken down to long chain fatty acids. – No COD reduction in
this step. Just shifts from solids into the liquid.
 |
fig: Hydrolysis process |
Acidogenesis -Anaerobic digestion
Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) are produced; generally produced from lipids.
 |
| fig: Acidogenesis process |
• Hydrogen production from fermentation is small, majority
of hydrogen arises from oxidation of VFAs (up to 6 carbon acids) and long chain
fatty acids to acetic acid, through the action of obligate anaerobes. This
process is called anaerobic oxidation.
 |
fig: Acidogenesis process |
• Anaerobic oxidation:
– Electron acceptor is H+ and it is converted to hydrogen
gas.
– Anaerobic oxidation is inhibited by hydrogen gas. For high
hydrogen gas partial pressures, reaction becomes thermodynamically unfeasible.
Final end product would be VFAs.
Acetogenic -Anaerobic digestion
Organic acids and alcohols are converted into acetic acid,
hydrogen and carbon dioxide by acetogenic bacteria. It is important that the hydrogen produced is consumed by the methanogenic microorganisms, as too
much hydrogen inhibits the formation of acetic acid.
 |
fig: Acetogenic process |
Propionic acid: CH3(CH2)COOH + H2O → CH3COOH + CO2 + 3H2
Methanogenesis
For successful operation of anaerobic digestion, need to
continuously remove hydrogen.
 |
fig: Methanogenesis |
• Methanogens are strictly anaerobes. There are mainly two
groups of these organisms in digesters.
– H2 -oxidizing methanogens: Reduce CO2 using H2 as the
electron donor and forming methane
(CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O).
– Acetoclastic methanogens: Cleave acetic acid into methane
and CO2
(CH3COOH→ CH4 + CO2 ).
– About 2/3 of
methane produced is derived from acetate.
– Also methanol forming bacteria, may also use methanol
(CH3OH + H2 → CH4 + H2O
)
– Virtually all COD into digester will end up as methane,
and small amount in biomass, due to low yield Methanogenesis e.g.
Mathanobacillus omelianskii, Methanobacterium formicicum, Methanosarcina
barkerii, and Methanococcus vannielli
This step is Often the rate limiting step in anaerobic digestion of acids.






1 Comments
solar panels dallas tx Project Local residents and businesses can purchase solar power from this project through a new solar-sharing program called. This program allows residents to invest in this green energy source by purchasing shares of electricity that are generated by their own rooftop panels, or through panels installation on the roof of the XL Center.
ReplyDelete